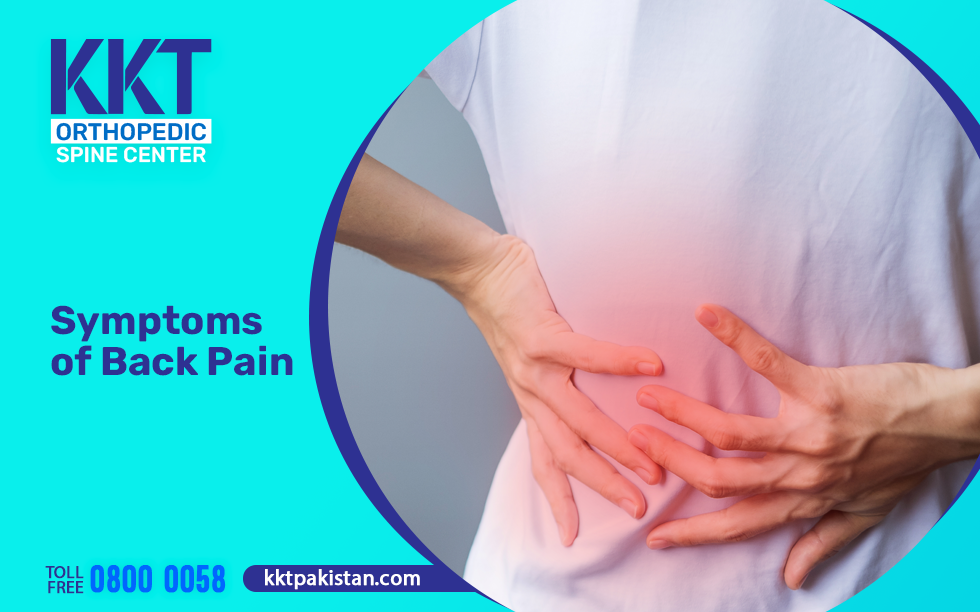
Back pain is a global health issue that affects individuals of all ages, making it one of the leading causes of inefficiency and work absences globally. Certain professions, particularly those involving sports, heavy lifting, or repetitive motions, carry an increased risk of developing back pain.
It is crucial to recognize the early signs of back pain; otherwise, it may develop and cause further spinal complications, deteriorating spinal health. Some severe backache symptoms, such as chronic pain that does not improve with over-the-counter medications, pain that radiates, numbness, stiffness, or reduced mobility, must not be overlooked and require prompt medical attention.
Kinds of Backache
Back pain is categorized into four types: acute, chronic, localized, and radiating. Symptoms and the duration of discomfort vary depending on the kind of pain.
- Acute pain is sudden, sharp pain resulting from injury, such as a slipped disc, muscle strain, or sports injury.
- Chronic pain persists over an extended period. This type of pain lasts for three months or more. Chronic back pain is often related to degenerative conditions such as arthritis, spinal stenosis, and disc degeneration.
- Localized pain is confined to a specific part of the spine and results from spinal misalignment, muscle strain, or ligament sprain.
- Radiating pain radiates from the back to the lower body from the buttocks, legs, and calves. The primary reason for this type of pain is sciatic nerve compression.
Common Symptoms of backache
Back pain can take a toll and affect one’s quality of life. Symptoms depend on the underlying condition of back pain that can manifest in various ways. These include:
- Dull or Aching Pain is persistent and often felt in the lumbar region. It does not relieve itself even with rest.
- Sharp or Stinging Pain is often localized and occurs suddenly due to muscle strain or injury. It intensifies with movement and can radiate to other body parts, such as the legs and buttocks.
- Muscle Stiffness or Tension in spinal muscles makes it difficult to move or bend. It is a common symptom of back pain. You might experience this after a prolonged period of inactivity.
- Numbness or Tingling: Back pain is often accompanied by a numbness and tingling sensation, specifically when nerve compression occurs. This is frequently associated with conditions like a herniated disc, sciatica, or spinal stenosis.
- Pain that worsens with activity: Some forms of back pain are exacerbated by specific activities such as walking, standing for an extended period, or sitting in a particular position.
- Limited range of motion: People with back pain may struggle to move, bend, or stand up straight. Activities like twisting, bending, or lifting heavy weights can be particularly painful and restrict body movement.
Backache Symptoms By Region
The back is categorized as cervical, thoracic, and lumbar, called the upper, middle, and lower back. Below are the different causes and specific symptoms for each region of the backache.
Cervical Pain
Seven vertebrae in the upper back form the neck and support the nerves that exit from the brain. You may experience localized pain in the neck and shoulders with a limited range of motion. Potential symptoms of upper back pain are:
- Stiffness or aching in between shoulder blades.
- Pain that worsens with movement.
- Limited range of motion of neck and shoulders
- Muscles spasms
Poor posture, muscle strain, herniated discs, arthritis, and scoliosis are potential causes of upper back pain. Fortunately, various ways exist to relieve mild and dull upper pain at home.
Thoracic Back Pain
Twelve vertebrates in total form the middle back that connects to the ribs. You may experience dull, burning pain that radiates towards your chest. Potential symptoms of middle back pain are as follows:
- Dull burning pain in the middle back region
- Pain radiating to the chest or ribs
- Limited range of motion
- Muscle tightness
- Numbness or tingling
- Stiffness
Potential causes of middle back pain are muscle strain, poor posture, inappropriate lifting techniques, herniated or bulging discs, degenerative disc disease, nerve compression, and spinal fractures.
Lumbar Back Pain
Five vertebrates in the lower back pain support the upper part of the spine. Lower back pain is common these days. Its symptoms involve:
- Sharp stabbing pain in the lower back
- Pain that radiates down into the buttocks, legs, and feet.
- Difficulty standing up straight or sitting for long periods
- Limited flexibility in the lower back.
- Muscle spasm
- Numbness, weakness
- Loss of bowel control
Potential causes of middle back pain are muscle strain, ligament sprain, herniated disc, sciatica, spinal stenosis, osteoarthritis, spondylolisthesis fractures, and trauma.
Symptoms Associated with Specific Conditions
Chronic lower back pain, accompanied by specific symptoms, can result from underlying conditions such as herniated discs, sciatica, osteoporosis, and scoliosis.
- Herniated Discs: when a disc between your vertebrae protrudes or ruptures, it compresses surrounding nerves, causing back pain, numbness, and weakness.
- Sciatica occurs when the sciatic nerve is compressed, often due to a herniated disc. The pain radiates from the lower back down through the legs.
- Osteoporosis is the degeneration of bones that reduces their density, making them more susceptible to fractures. Its symptoms include chronic back pain, spine malformation, and a hunched back.
- Scoliosis is an abnormal curvature of the spine that can lead to chronic back pain, especially as people age.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Most cases of back pain improve with home remedies, self-care, and time, but specific symptoms require immediate medical attention. These include
- Pain that persists for more than a week.
- Severe pain that does not improve with rest.
- Pain accompanied by unexplained weight loss.
- Weakness, numbness, tingling sensation in legs.
- Loss of bladder or bowel control.
These symptoms indicate more serious underlying conditions, such as spinal infection or sciatica, that require medical care.
Lifestyle Choices that Agonize Backache
Our daily habits decide the quality of our lives. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and maintaining an upright body posture are all minor details that play a comprehensive role in our lives.
Role of posture
Sitting, standing, or walking with poor posture over time can lead to back pain, rounded shoulders, and spinal dysfunction. Proper posture can reduce the wear and tear of joints and avoid common aches such as back, shoulder, and neck pain.
For optimal spinal health, maintain proper posture throughout physical activities, prefer ergonomic furniture, and avoid twisting the spine.
Impact of physical activity and exercise
Regular physical activity strengthens the muscles supporting your spine and alleviates back discomfort. Incorporate physical activities and exercises into your daily lifestyle to strengthen abdominal muscles and ease pain.
Low—impact exercises, such as bridges, planks, walking, swimming, and stretching, can ease lower back pain, maintain flexibility, and reduce stiffness. Avoid intense workouts during back pain. Adapt proper weight-lifting techniques to avoid slipped discs.
Effect of obesity on the spine
Excessive weight or obesity puts pressure on the spine. It disturbs its natural curvature, causing herniated discs and pinched and compressed nerves. Losing weight can reduce pressure on the spinal vertebrae and lessen the inflammation.
Maintain a healthy weight and adapt to a healthy lifestyle to improve physical and mental health. Avoid junk food, and fulfill the daily nutrient count that the body requires. This will boost immunity and strengthen spinal muscles to provide better support to the spine.
Conclusion
Back pain is common nowadays due to poor habits and a sedentary lifestyle. Specific back pain symptoms are present based on the back’s location. Backache is categorized as acute, chronic, radiating, or localized pain. Early detection of backache symptoms is necessary to avoid further spinal health complications. Everybody experiences backache at some point in their lives, but one must remember not to ignore the severe symptoms as they happen due to some underlying conditions.
- Chronic pain
- Loss of sensation
- Weakness, numbness, and tingling sensation
- Loss of bowel control
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
How do I know if my back pain is severe?
If back pain does not go away with rest and persists, accompanied by restricted body movement, weight loss, and loss of bowel control, contact a healthcare professional right away.
What are the symptoms of acute vs chronic back pain?
Acute back pain symptoms involve a dull, mild backache. Chronic back pain symptoms are sharp, stabbing pain that persists for over three weeks.
What Symptoms of Back Pain in Females?
The symptoms of back pain in males and females are the same. However, the causes can differ. Some symptoms include stiffness, muscle spasm, sprain, or strain of ligaments and muscles.
Types of Back Pain.
Back pain is categorized into four types: chronic, acute, localized, and radiating.
Lower Back Pain Symptoms for Pregnancy.
During pregnancy, women often feel pain in the pelvic area and lumbar spinal region due to increased pressure on spinal muscles.
PS: If you have chronic back pain, schedule an appointment with the expert team of consultants at KKT Orthopedic Spine Center onboard.